
The global automotive landscape is undergoing a rapid transition toward electrification, and Honda Motor Company is strategically positioning its intellectual property portfolio to lead this shift. Recent developments indicate that the Japanese manufacturer has submitted a significant patent filing for a new electric commuter motorcycle. This move underscores Honda’s commitment to expanding its electric vehicle (EV) footprint beyond scooters and into the high-volume entry-level motorcycle segment.
Understanding the Honda Electric Commuter Motorcycle Patent
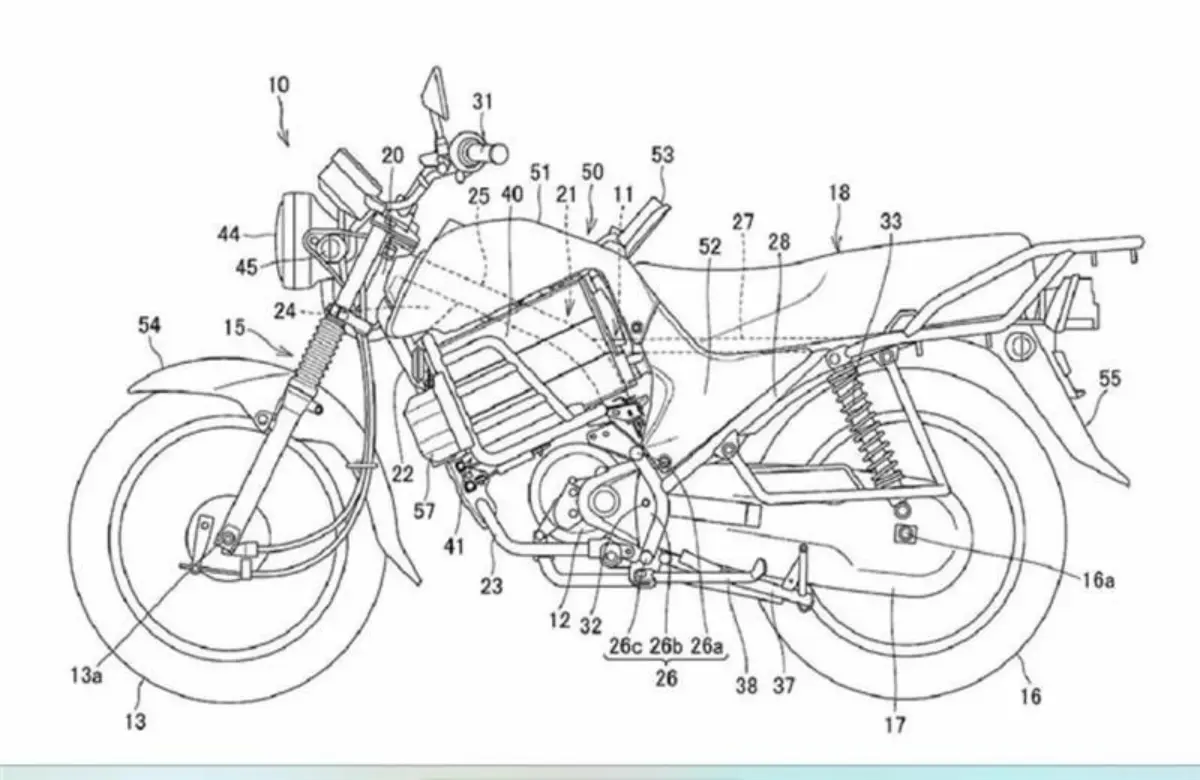
The Honda Electric Commuter Motorcycle Patent reveals a design focused on functional simplicity and mass-market accessibility. Unlike high-performance electric concepts that prioritize speed and luxury, this filing details a pragmatic approach to urban mobility. The technical drawings associated with the Honda Electric Commuter Motorcycle patent suggest a machine built on a basic backbone frame, a structural choice typically favored for its cost-effectiveness and durability in commuter motorcycles.
The design incorporates conventional hardware to ensure ease of maintenance and reliability. According to the patent filing, the motorcycle features:
- A traditional telescopic front fork.
- Twin rear shock absorbers.
- Drum brakes at both the front and rear ends.
- A classic round headlamp assembly.
These design choices reflect a strategic alignment with the aesthetics of successful internal combustion engine (ICE) commuters, such as the legendary Honda Shine or the CD series. By utilizing familiar mechanical layouts, Honda aims to reduce the barrier to entry for traditional riders transitioning to electric propulsion.
Read Also: Capacity Building in Intellectual Property for the Sri Lankan Judiciary: IP Benchbook Launch
Technical Innovations and IP Protection
A critical component of this Honda Electric Commuter Motorcycle patent is the powertrain configuration. The documents illustrate an electric motor integrated with a system designed for removable battery packs. This focus on battery-swapping technology is a cornerstone of Honda’s electrification strategy. By securing IP protection for this specific configuration, Honda ensures its proprietary methods for battery integration and housing remain legally shielded from competitors.
The patent images further highlight a unique instrumentation setup. The motorcycle appears to feature a primary, slightly offset round instrument cluster, complemented by a secondary display unit mounted atop the area traditionally reserved for a fuel tank. This secondary interface is likely dedicated to providing real-time telemetry regarding battery state-of-charge (SoC) and energy consumption, which are vital metrics for EV operators.
Strategic Importance of the Patent Filing
In the competitive landscape of the automotive industry, a patent filing serves as more than just a technical blueprint; it is a vital tool for IP protection. By registering these designs, Honda prevents unauthorized use of its technical innovations and design language. This is particularly important in emerging markets where entry-level electric motorcycles are expected to see exponential growth.
Key strategic takeaways from the recent Honda electric motorcycle patent include:
- Market Localization: The hardware specifications suggest a product optimized for markets with diverse road conditions, emphasizing ruggedness over complex electronics.
- Infrastructure Coordination: The reliance on removable batteries aligns with Honda’s ongoing investment in battery-swapping stations, creating a cohesive ecosystem for the end-user.
- Platform Versatility: This filing follows a previous patent for an electric motorcycle based on the Honda Shine 100 platform, indicating that Honda is exploring multiple design avenues to capture different sub-segments of the commuter market.\
Read Also: Copyright Protection for AI-Generated Artworks: Legal Perspectives
Legal and Commercial Implications
It is essential to note from an IPR perspective that while a patent filing grants the applicant exclusive rights to the invention for a set period, it does not guarantee that the specific design will enter immediate mass production. However, the level of detail regarding the frame and battery housing in the Honda electric motorcycle patent indicates an advanced stage of research and development.
The pursuit of IP protection for these designs signals to investors and competitors that Honda is securing its “right to play” in the electric motorcycle space. By formalizing these technical solutions through a patent filing, Honda establishes a legal priority date, which is crucial in potential patent infringement litigation.
Conclusion
The emergence of the Honda electric motorcycle patent highlights the manufacturer’s systematic approach to the EV transition. By focusing on the commuter segment through robust hardware and swappable battery technology, Honda is addressing the core requirements of urban riders. As the company continues to bolster its IP protection through strategic filings, the automotive industry awaits the formal Patent commercialization of these patented technologies, which could redefine the entry-level electric two-wheeler market.
